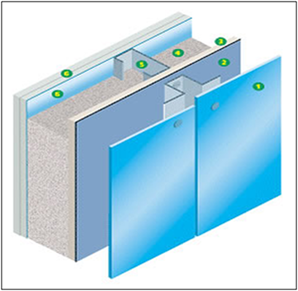
exterior cladding is the first barrier prevention from the elements such as weather and sound. Exterior cladding tends to be more than one material for instance external layer, moisture and insulation barriers and another layer for internal protection.
Detail
exterior Insulation
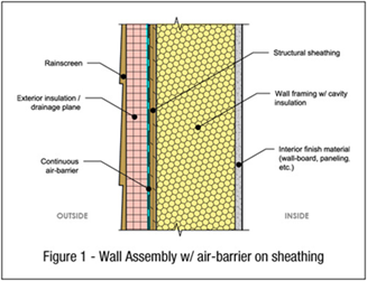
this layer helps keep water vapor in the air from condensing inside the wall, as well as dramatically improving overall R-value of the wall. Water vapor is bound to get into the wall somehow, so the goal here is to prevent it from condensing into liquid water. Liquid water inside walls leads to rot, loss of insulating value and MOLD. Mold is very dangerous to your health. The exterior insulation should be a closed cell foam; if the insulation also acts as the drainage plane, it should also be impervious to liquid water. Extruded polystyrene like Owens Corning Foamular 150 is a good choice. All seams and penetrations should be sealed and taped according to manufacturer installation instructions.
Continuous Air Barrier
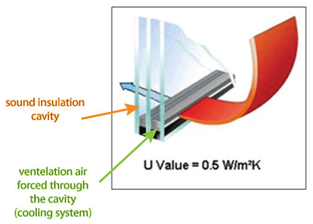
the greatest potential source of heat loss through a wall or roof is air infiltration (leaks). Although some foam insulations may claim to be air-tight, it is a good idea to include a separate air-barrier membrane. House-wraps like Tyvek and Typar, Raindrop are the most commonly used air-barriers. They can go on the exterior of the sheathing (figure 1) or the exterior of the rigid board insulation depending on your choice of drainage plane and window installation. The air-barrier must be sealed at all openings, corners and edges so that no air leakage is possible through the wall. Even the smallest pin hole can seriously degrade the performance of the wall and allow moisture to get through. It you take a pen and draw the air-barrier on any section through the house, that line should have no gaps in it. Ideally, if there is anywhere for moisture to condense in the walls, it should be outside this air barrier.
Weathering Surface
this layer, sometimes referred to as a rainscreen or cladding, keeps wind-driven rain, ice and other bulk water out of the wall, as well as protecting other building materials from exposure to UV-radiation. Siding, brick and stucco are all common examples of primary weathering surfaces. Consult the product manufacturer installation instructions regarding ventilation requirements; wood siding, for example, will last longer if there is a ventilation space behind it. This space can be achieved using furring strips or products likeHomeSlicker.
this layer helps keep water vapor in the air from condensing inside the wall, as well as dramatically improving overall R-value of the wall. Water vapor is bound to get into the wall somehow, so the goal here is to prevent it from condensing into liquid water. Liquid water inside walls leads to rot, loss of insulating value and MOLD. Mold is very dangerous to your health. The exterior insulation should be a closed cell foam; if the insulation also acts as the drainage plane, it should also be impervious to liquid water. Extruded polystyrene like Owens Corning Foamular 150 is a good choice. All seams and penetrations should be sealed and taped according to manufacturer installation instructions.
Continuous Air Barrier
the greatest potential source of heat loss through a wall or roof is air infiltration (leaks). Although some foam insulations may claim to be air-tight, it is a good idea to include a separate air-barrier membrane. House-wraps like Tyvek and Typar, Raindrop are the most commonly used air-barriers. They can go on the exterior of the sheathing (figure 1) or the exterior of the rigid board insulation depending on your choice of drainage plane and window installation. The air-barrier must be sealed at all openings, corners and edges so that no air leakage is possible through the wall. Even the smallest pin hole can seriously degrade the performance of the wall and allow moisture to get through. It you take a pen and draw the air-barrier on any section through the house, that line should have no gaps in it. Ideally, if there is anywhere for moisture to condense in the walls, it should be outside this air barrier.
Weathering Surface
this layer, sometimes referred to as a rainscreen or cladding, keeps wind-driven rain, ice and other bulk water out of the wall, as well as protecting other building materials from exposure to UV-radiation. Siding, brick and stucco are all common examples of primary weathering surfaces. Consult the product manufacturer installation instructions regarding ventilation requirements; wood siding, for example, will last longer if there is a ventilation space behind it. This space can be achieved using furring strips or products likeHomeSlicker.
Frame work
Aluminium frame
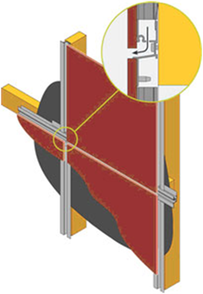
- The rail system combines ease of installation with drained and vented cavities at every express joint.
- designed to be used as an external wall
- drained and vented cavities
- eliminating any possibility of screws popping and allows for pre-finished cladding sheets including a clear seal.
- Frame work lightweight due to the material used.
- tends to be used within rain screen cladding
Structural glazing individual frames
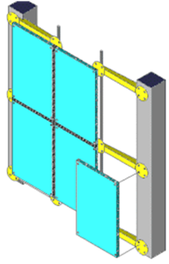
Structural glazing comprises frameless glazing in which each glazing unit is supported by point fixings, normally bolted connections.
The glazing units may be supported individually from a separate framed structure similar to that shown or a stick construction curtain wall. Walls of this type are frequently called 'Planar' walls although 'Planar' is a brand name and other products exist.
In true structural glazing the glass components transfer load. It may comprise glazing units suspended one from another or glazing units supported from glass fins or portals.
Structural silicone glazing
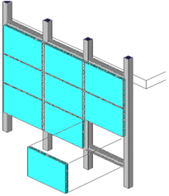
Structural sealant glazing is a method of bonding the glazing units to a frame. This has the advantage that the glazing appears from the outside to be frameless.
In practice the glazing is bonded to a carrier frame that is bolted to a framing system such as that for a stick construction curtain wall.
The glazing may be bonded on two edges (and framed on the other two) or it may be bonded on four edges. In the latter case small clips may be provided to provide mechanical retention.
In practice the glazing is bonded to a carrier frame that is bolted to a framing system such as that for a stick construction curtain wall.
The glazing may be bonded on two edges (and framed on the other two) or it may be bonded on four edges. In the latter case small clips may be provided to provide mechanical retention.
Rainscreen
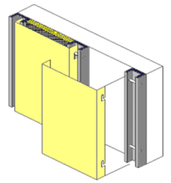
Rainscreen is a plane of panels designed to protect the wall from rain. It may be constructed as overcladding supported on a brick or block wall or as an integral wall supported from mullions or studs spanning from floor to floor.Rainscreen overcladding is often used on refurbishment projects but may be used to advantage when constructing new buildings.
Integral rainscreen walls supported from framing members are dependent on an inner air barrier to carry wind load and give the required air permeability.
Insulated panels
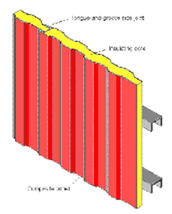
Insulated panels comprise a a layer of insulation faced with metal or plastic sheets. The perimeter comprises a profile that enables them to interlock to provide a sealed structural connection.
Insulated panels may be manufactured with windows installed but more normally windows are installed at site as the wall is assembled.
Insulated panels have to be supported from a framework of columns and/or purlins. Profiles are often available to allow the use of different window systems as part of an insulated panel system.